Biphasic Mesothelioma
Biphasic mesothelioma occurs when epithelial and sarcomatoid mesothelioma cells are present in one tumor. A biphasic meosthelioma patient’s prognosis (health outlook) depends on which cell type is more dominant in the tumor, the cancer’s location, and other factors. Learn more about biphasic mesothelioma, its prognosis, and treatments below.
What Is Biphasic Mesothelioma?
Biphasic mesothelioma is the second-most common mesothelioma cell type. It accounts for 20-30% of mesothelioma cases, according to the American Cancer Society.
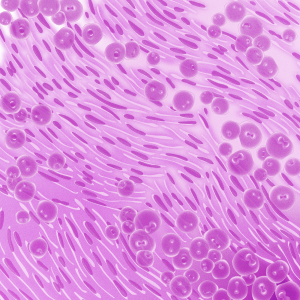
Also known as mixed mesothelioma, biphasic mesothelioma tumors consist of both epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells, which are the two other mesothelioma cell types.
Each mesothelioma cell type has unique characteristics:
- Epithelial mesothelioma cells, or epithelioid mesothelioma cells, are rectangular in shape and take longer to spread throughout the body.
- Sarcomatoid mesothelioma cells are thin, spindle-shaped cells that replicate slower but can easily spread to distant parts of the body.
The prognosis of biphasic mesothelioma varies for each patient because each case will have a different ratio of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells making up the biphasic mesothelioma tumor.
Biphasic patients with a higher amount of sarcomatoid cells have a poor prognosis as this cell type is more aggressive and harder to treat with surgery.
For help with biphasic malignant mesothelioma, download our Free Mesothelioma Guide today. The guide includes information on life expectancy, treatment options, and financial assistance.
 Free 2024 Mesothelioma Guide
Free 2024 Mesothelioma Guide- Find Cancer Resources
- Get Medical Care
- Access Compensation


Symptoms of Biphasic Mesothelioma
Biphasic malignant mesothelioma does not have its own unique symptoms. Instead, biphasic mesothelioma symptoms depend on the location of the tumor.
This is because any type of mesothelioma — pleural, peritoneal, pericardial, or testicular — can be categorized as biphasic mesothelioma.
Symptoms for each type of biphasic mesothelioma include:
- Pleural mesothelioma, which develops in the pleura or lining of the lungs, causes shortness of breath and a persistent cough.
- Peritoneal mesothelioma, which develops in the stomach, causes bloating and nausea.
- Pericardial mesothelioma, which develops in the heart, causes chest pain and difficulty breathing.
- Testicular mesothelioma, which develops in the tunica vaginalis or thin lining of the testicles, causes swelling and pain.
Causes of Biphasic Mesothelioma
Like all types of mesothelioma, the only known cause of biphasic mesothelioma is asbestos exposure.
When asbestos fibers are released into the air, you may breathe them in or ingest them Unfortunately, once in the body, asbestos fibers cannot break down or be removed.
Over time, the fibers cause scarring and inflammation of the mesothelium, the thin layer of tissue that protects the heart, lungs, and stomach. This can cause the DNA of the mesothelial cells to mutate and grow out of control, leading to cancer.
It’s not known at this time why some people develop biphasic mesothelioma and others develop other mesothelioma cell types.
Diagnosing Biphasic Mesothelioma
There are several diagnostic tests oncologists will run before diagnosing a patient with biphasic mesothelioma.
These diagnostic tests are typically given in this order:
- Imaging tests: These provide detailed images of the body through X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs to determine where mesothelioma cells may be present.
- Blood tests: Often performed around the same time as imaging tests, blood tests measure certain biomarkers to see if mesothelioma may be present in the body.
- Biopsies: Doctors remove a fluid or tissue sample from the body to test in a lab. Pathologists will then run immunohistochemistry tests to understand the cells present in the sample.
Biopsies are the only way to confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis and the only way to determine the mesothelioma cell type present. During immunohistochemistry tests, doctors may also be able to determine the amount of epithelioid or sarcomatoid mesothelioma cells present.
Sometimes, biphasic mesothelioma patients may have to undergo multiple biopsies because doctors will need to completely show the presence of both epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells.
Biphasic Mesothelioma Prognosis
The prognosis for biphasic mesothelioma varies depending on the predominant type of cells in the tumor.
For example, biphasic mesothelioma patients whose tumors consist of 20% or more epithelioid cells typically have a better prognosis. This is because epithelioid cells respond better to surgeries and other treatments.
According to a study from the open research journal F1000, the average life expectancy for biphasic mesothelioma is 10 months. This is just slightly better than sarcomatoid mesothelioma, which has a median survival of 7 months.
Getting treatment from a mesothelioma specialist is key to living as long as possible with any type of mesothelioma. You may even be able to outlive the average life expectancy, depending on how your cancer responds to treatment.
Contact our team today, and we can help you find a mesothelioma specialist near you.
Treatments for Biphasic Mesothelioma

There are several different biphasic mesothelioma treatment options. Each malignant biphasic mesothelioma patient will require unique treatments depending on multiple factors.
These factors include:
- Location/type of the mesothelioma cancer
- Patient’s overall health
- Ratio of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells
- Stage of mesothelioma
Learn about possible treatments for biphasic malignant mesothelioma below.
Chemotherapy
Mesothelioma chemotherapy uses drugs to kill fast-growing cancer cells in the body. It can be an effective way to treat mesothelioma throughout the body, and it is even more effective when coupled with surgery.
Common chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma include:
- Carboplatin
- Cisplatin
- Pemetrexed
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy was recently approved for mainstream treatment of mesothelioma. Mesothelioma immunotherapy uses immune-boosting drugs to help the immune system target and kill mesothelioma cells.
Common mesothelioma immunotherapy drugs include:
- Ipilimumab
- Nivolumab
- Pembrolizumab
Biphasic immunotherapy is often given in combination with other treatment options, including surgery and chemotherapy.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses powerful X-rays to kill mesothelioma cells. Radiation therapy is not often used alone to treat mesothelioma. Instead, providers often use it as part of a multimodal treatment plan, combining it with chemotherapy and surgery.
Surgery
Surgery allows doctors to remove any visible biphasic mesothelioma tumors from the body.
Common mesothelioma surgeries include:
- Cytoreduction with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC)
- Extrapleural pneumonectomy
- Pleurectomy with decortication
Biphasic mesothelioma tumors that are mainly made up of epithelioid cells tend to be easier to treat with surgery. This is because epithelioid cells tend to clump together, making it less likely for cells to break off and spread throughout the body.
Clinical Trials for Biphasic Mesothelioma
Clinical trials for mesothelioma are research studies with human volunteers that evaluate the effectiveness of new treatment methods.
Many patients have seen positive results after participating in mesothelioma clinical trials. In fact, many researchers are exploring new treatment options for those with biphasic mesothelioma.
Talk with your mesothelioma specialist to see if there are clinical trials you might qualify for.
Find Help Getting Treatment for Biphasic Mesothelioma
Receiving a biphasic mesothelioma diagnosis is life-changing, and many people may feel overwhelmed and anxious.
If you or a loved one have been diagnosed with biphasic mesothelioma, Mesothelioma Resource Group is here to help. We can connect you with oncology providers, top treatments, and financial assistance.
Get a free mesothelioma guide now to see how we can help you.
Biphasic Mesothelioma FAQs
Biphasic mesothelioma is the second-most common cell type of this cancer. It accounts for 20% to 30% of all mesothelioma cases. It occurs when a mesothelioma tumor has both epithelioid and sarcomatoid mesothelioma cells.
How effective treatment is for biphasic mesothelioma will depend on the predominant cell type in the tumor. For example, biphasic tumors that have higher numbers of epithelioid mesothelioma cells are more likely to be eligible for resection (treatable through surgery).
The best treatment option for biphasic mesothelioma will depend on each patient’s specific diagnosis, their overall health, and other factors.
Most often, multimodal treatment plans (where more than one treatment is combined) can be provided by oncologists. It is important to work with a mesothelioma specialist to determine the best treatment plan for you.
The prognosis for biphasic mesothelioma varies depending on the ratio of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells. Generally speaking, biphasic mesothelioma patients have an average life expectancy of 10 months.
At this time there is not an official cure for mesothelioma. However, it is possible for people to live for years or even decades following their diagnosis. It’s important to find a mesothelioma specialist and seek out the best treatment plan for your diagnosis as early as possible.
Yes. While it is rare, biphasic mesothelioma can go into remission. The earlier a patient is diagnosed and receives treatment the more likely they are to enter remission. This is because the cancer was likely caught before it spread, or metastasized, to distant parts of the body.
